BASF – Ultrafuse ABS Filament – Red Nagase Specialty Materials
$ 29,95 $ 17,97
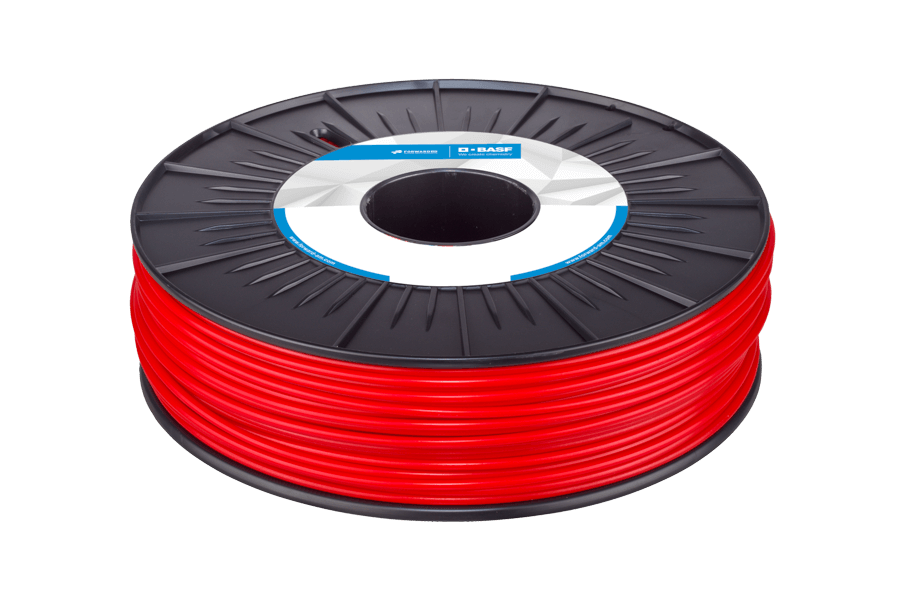
Ultrafuse® ABS
ABS is the second most used 3D printing material
Strong, flexible and has a high heat resistance. ABS is a preferred plastic for engineers and professional applications. ABS can be smoothened with acetone. To make a proper 3D print with ABS you will need a heated print bed. The filament is available in 9 colors.

Benefits at a Glance
- Long life span
- Very tough
- High wear and tear
- Can be used for working parts
- Chemical resistance
Example Applications
- Functional prototypes
- Chemical environment
- Reasonable heat resistance
Material Properties
- Tensile Strength (MPa): 21.3 (ZX), 36.3 (XY)
- Flexural Modulus (MPa): 1587 (ZX), 1767 (XZ), 1833 (XY)
- Elongation at Break: 1.8 % (ZX), 7.4 % (XY)
- Impact Strength Izod notched (kJ/m2): 3.5 (ZX), 18.9 (XZ), 18.8 (XY)
- Impact Strength Izod unnotched (kJ/m2): 7.2 (ZX), 35.7 (XZ), 40.0 (XY)
- HDT @ 0.45 MPa: 96 oC
Printing Guidelines
- Nozzle Temperature: 240-260 °C
- Build Chamber Temperature: –
- Bed Temperature: 90 – 110 °C
- Bed Material: Tape, Spray, Glue
- Nozzle Diameter: ≥ 0.4 mm
- Print Speed: 40-80 mm / s
Next Steps
Printing Profiles
- Ultimaker
- Raised 3D
- Prusa
- BCN3D
Material Details
- Techincal Data Sheet
- Saftey Data Sheet
| Diameter | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
|---|---|
| Spool Size | 750g |
Professional packing and fast shipping
Due to our longstanding partnership with UPS FedEx DHL and other major global carriers, we are able provide a range of shipping options. Our warehouse staff is highly trained to package your goods exactly as per the specifications we offer. Before shipping the goods are carefully inspected and secured. Everyday we deliver thousands of packages to customers from all over the world. This is a testament to our commitment to be the largest online retailer worldwide. The warehouses and centers for distribution are situated in Europe and the USA.
Orders with more than one item are given processing time for each item.
Before shipping, we will conduct a thorough inspection of the items you've ordered. Currently, most orders are shipped within 48-hours. Expected delivery time is between 3 and 7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we do not fully manage it because of the fact that multiple stakeholders are involved, including our factory and warehouse. The actual levels of stock can change at any moment. It's possible that the stock may run out after your order has been placed.
The policy is 30 days. If you haven't received the product within 30 days, we are not able to issue a refund or an exchange.
For your item to be returned, it must be unopened and in the same state as you received it in. It must also be in the original packaging.
Related products
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer
3D Printer